Conflict in Sudan
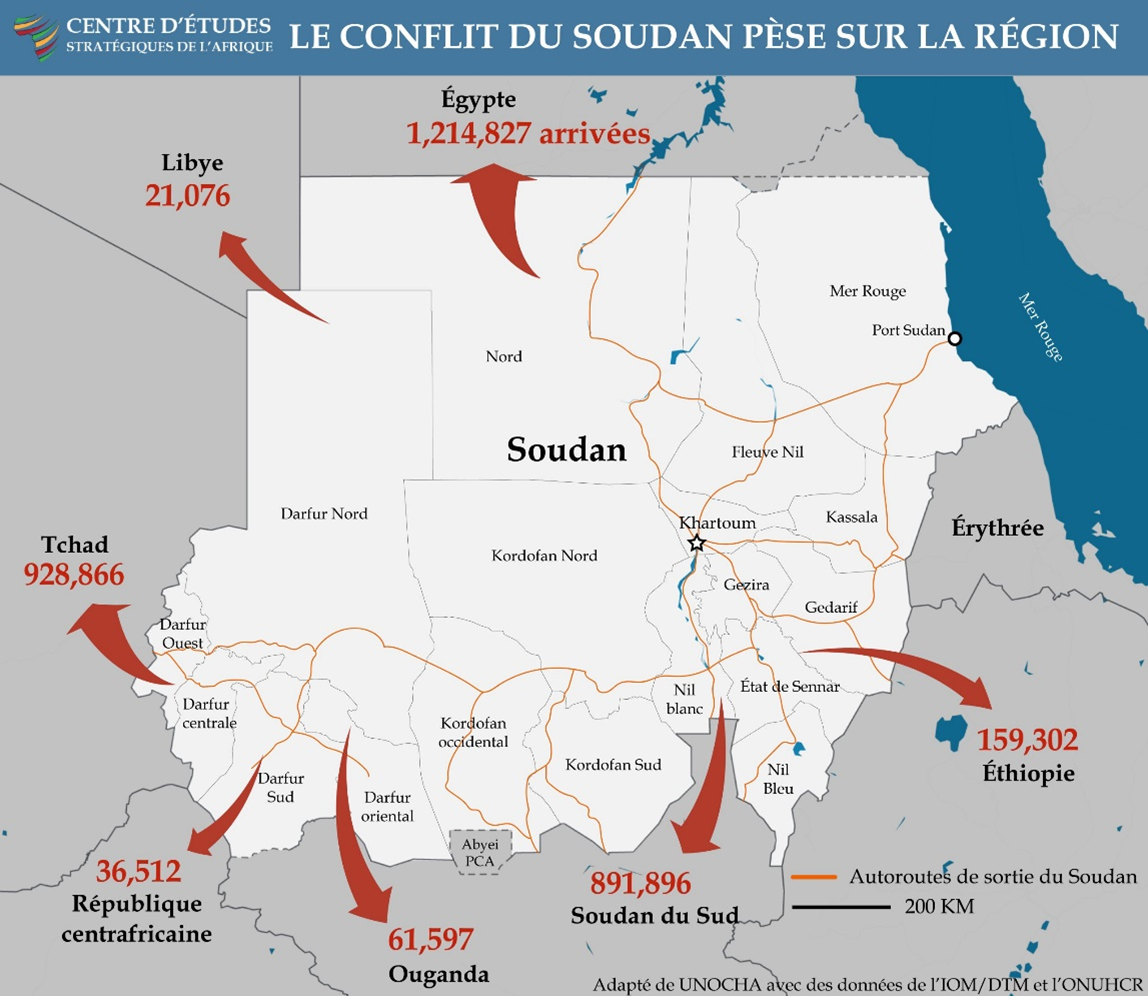
The conflict between rival military factions in Sudan has resulted in the world’s largest displacement crisis. More than 11.5 million people are internally displaced and more than 2.3 million have fled the country since the war began in April 2023. Food shortages and famine are estimated to be killing hundreds of people every day. An estimated 3 million people are also facing acute food insecurity this year.
Sudan’s implosion has reverberated across the already fragile region, multiplying conflict and instability in neighboring countries. Instability in Sudan only further complicates internal conflicts in Libya, Chad, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, and Ethiopia.
Foreign powers including the United Arab Emirates, Russia, Iran, and Egypt are stoking conflict in Sudan by deploying drones, munitions, mercenaries, and smuggling resources. This scramble for regional influence threatens to transform Sudan into a collection of client states where civilian voices and popular sovereignty are sidelined.
Protecting the Congo Basin from Illegal Logging
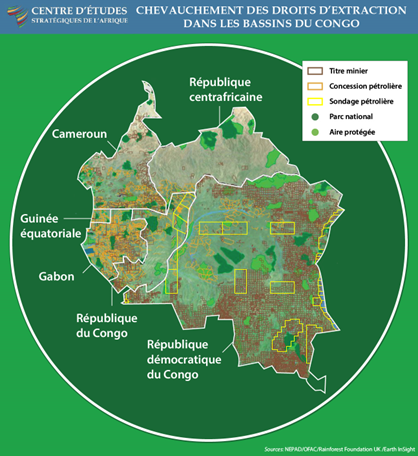
The Congo Basin rainforests account for about 70% of Africa’s forest cover, making it the world’s largest terrestrial carbon sink. The Congo Basin is critical to the water cycles that sustain the Nile Basin and West Africa. But only 14% of its area has protected status, and the basin has lost 1% of its forest cover since 2001, largely due to unregulated commercial and mining logging. Congo Basin forests are declining by 1–5% per year.
Protecting the Congo Basin, its ecological resources, and the millions of livelihoods it supports is a regional security imperative with continental and global implications. Transnational criminal networks are taking advantage of the region’s weak forest management to plunder this rich resource.
Improving the management and protection of the Congo Basin’s tropical forests will require improved knowledge of the forest domain and a realignment of incentives for local communities, government officials, and international logging interests.
Maritime Vulnerability in the Red Sea and Western Indian Ocean
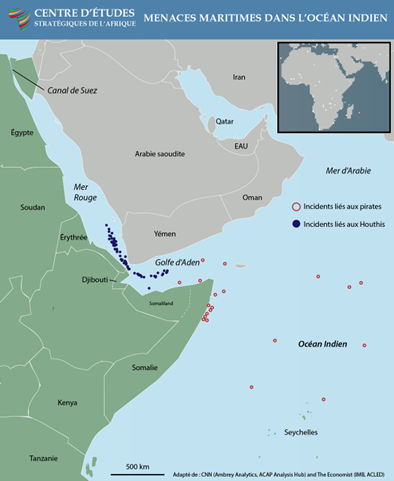
More than 100 sabotage and pirate attacks on ships in the Red Sea and the western Indian Ocean have exposed the vulnerability of African maritime security. Attacks by the Houthi militia and Somali pirates are the main culprits behind the disruptions, which have disrupted shipping, sunk ships, and damaged undersea cables.
As a result of these attacks, African citizens have borne the cost in the form of delays, more expensive consumer goods, disruptions to local economies, and pollution of waterways from sunken munitions and ships in the Red Sea and western Indian Ocean.
The maritime security crisis in the Red Sea illustrates not only how actions by non-state actors can affect global economic dynamics but also that Africa is at the heart of global shipping.
Piracy and armed robbery at sea, however, declined in the Gulf of Guinea in 2024 to their lowest level in years, largely due to increased patrols and collaboration among members of the Yaoundé Protocol on Maritime Security.
For more information :
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portail:Afrique
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Africa
- https://africacenter.org/
- https://journals.openedition.org/etudesafricaines/
- https://etudes-africaines.cnrs.fr/
- https://journals.openedition.org/etudesafricaines/
- https://www.afdb.org/fr/documents-publications/economic-perspectives-en-afrique-2024